Audit plan definition - concepts
All inventory audit plans share certain global properties at the definition level:
All audit plans must have a duration and an interval which calculates the number of sessions.
Randon Sample and Continuous audit plans are broken down into scheduled tasks for the assigned counters.
For Inventory by Exception audit plans, there are no scheduled tasks for each counter; tasks are initiated by a trigger.
Random Sample and Continuous cycle audit plans
Random Sample and Continuous (scheduled) audit plans have the same task breakdown. The only difference between these two plans is the pool of inventory to be counted: Continuous is wall to wall and Random Sample takes a percentage of the pool of inventory. How the tasks are broken down and assigned based on the plan details does not differ.
The following illustration shows a Random Sample audit plan definition, the plan details, and the tasks to be done by each counter for each interval (None, Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Quarterly).
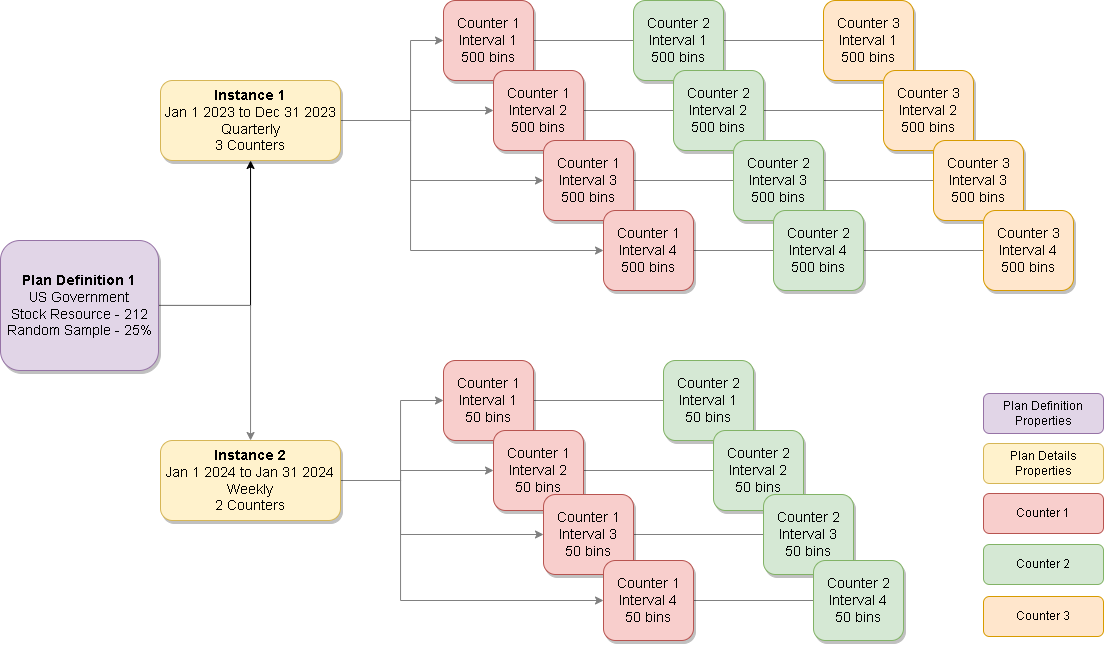
A pool of inventory is defined by various filter properties in the audit plan definition. The inventory pool comprises the defined plan details (where, when, and who) to schedule a series of tasks. Each task has an expectation of when it will be completed based on when the task was created (start of interval or mismatch count result) and the time period defined in the audit plan details.
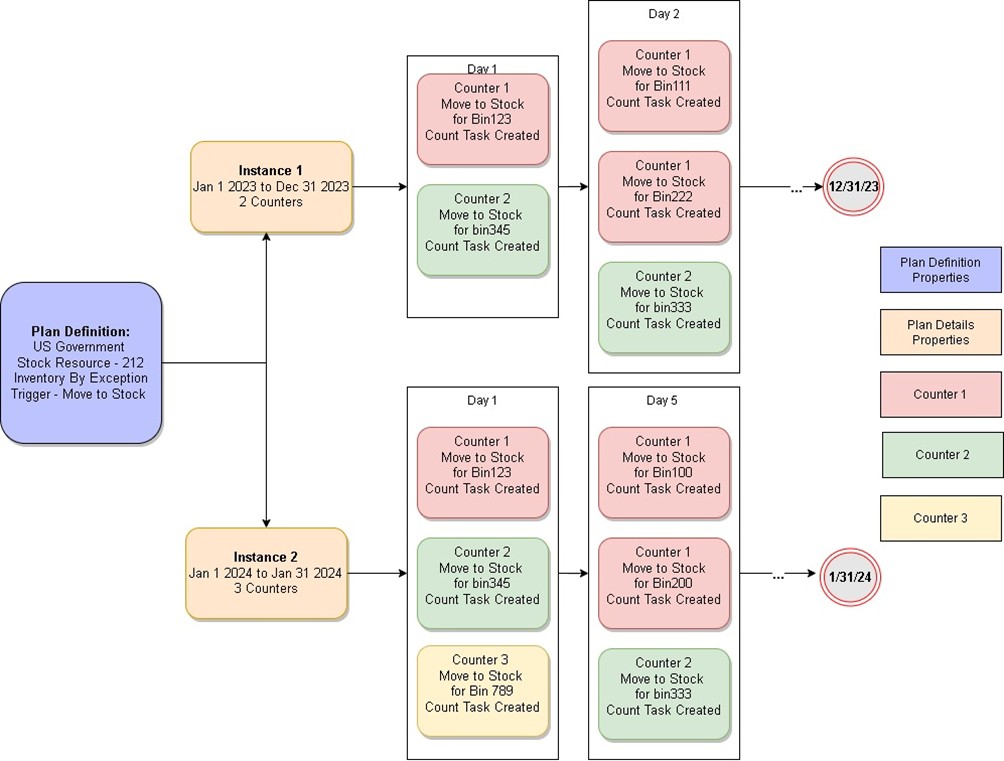
Inventory By Exception audit plans
Inventory by Exception audit plans are not scheduled and don’t have a fully planned out methodology as far as scheduling tasks for specific durations and intervals. Plan details are a part of the planning such as who, where, and when, but the creation of the task assignments is triggered by a material movement such as Move To Stock or Remove From Stock and expected to be done immediately whenever possible. The definition of the audit plan includes the details of what triggers the counting tasks, and the filters drive where and what to count.
The following illustration shows an example of how tasks get create, specifically how the tasks creation is based on a trigger that can happen at any time during the start date and end date of the audit plan. In this case, an operator only counts bins when a material movement is done on a particular bin that meets the requirements based on the plan setup.